Describe the Differences in the Four Protein Structures.
Identify examples of proteins. 3 - Aquaporins are proteins embedded in the plasma.

Structure Of Proteins Ck 12 Foundation
Primary Structure of Proteins.

. SECONDARY2 STRUCTURESare regular repeating structures that occur over short localized regions of the protein molecule. Explain how proteins result in an organisms traits. Proteins have different layers of structure.
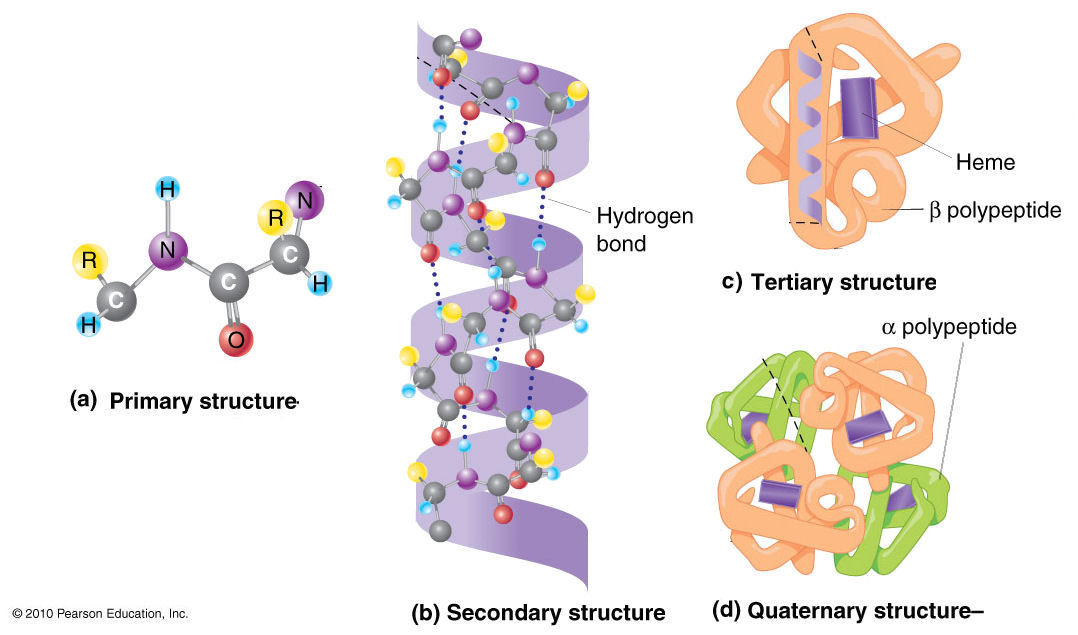
It is helpful to understand the nature and function of each level of protein structure in order to fully understand how a protein works. The four levels of protein are1 Primary Structure2 Secondary Structure3 Tertiary Structure4 Quaternary StructureThe primary structure is just the amino acids bonded to eachother in a linear. The levels are the hydrogen atom.
This native state can be disrupted by. Recognize that molecular structure determines molecular interactions and relates to the cellular functions of proteins. Biology Final Chapter.
Primary secondary tertiary and quaternary are the four structures of proteins found in nature. Explanation of the levels of protein structure Learn with flashcards games and more for free. The four levels of protein structure are shown in Figure 2.
This includes number of polypeptides number and sequence of amino acids in each polypeptide. The three-dimensional fold structure of most proteins. Get solutions Get solutions Get solutions done loading Looking for the textbook.
A The primary structure is the succession of amino acid residues usually abbreviated by the 1- or 3-letter codes. 3 - What are the four types of RNA and how do they. As a multitude of protein structures are rapidly being determined by Xray crystallography and by nuclear magnetic resonance NMR it is becoming clear that the number of unique folds is far less than the total.
Tertiary Structure The overall three-dimensional shape of a polypeptide due to interactions of the R groups of the amino acids making up the chain. Solutions for Chapter 3 Problem 32CTQ. The complete structure of a protein can be described at four different levels of complexity.
Proteins are constructed from 20 amino acids. PRIMARY1 STRUCTUREis the unique amino acid sequence of the protein. The primary structure is the sequence of amino acids that make up a polypeptide chain.
Four levels of Protein Structure. Due to the nature of the weak interactions controlling the three-dimensional structure proteins are very sensitive molecules. Name and describe the third level of protein structure.
20 different amino acids are found in proteins. For example the hormone insulin has two polypeptide chains A and B shown in diagram below. The four levels of protein structure are differentiated from each other by the complexity of their polypeptide chain.
Explain the relationship between amino acids and proteins. Primary secondary tertiary quaternary. Major functions include acting as enzymes receptors transport molecules regulatory proteins for gene expression and so on.
Proteins have a variety of function in cells. It is the description of basic structure of a protein. 3 - Explain what happens if even one amino acid is.
The main difference between primary secondary and tertiary structure of protein is that the primary structure of a protein is linear and the secondary structure of a protein can be either an α-helix or β-sheet whereas tertiary structure of a protein is globular. Describe the differences in the four protein structures. The different levels of protein structure are known as primary secondary tertiary and quaternary structure.
Four Levels of Protein Structure. The four levels of protein structure are primary secondary tertiary and quaternary. Primary secondary tertiary and quaternary structure.
3 - Describe the differences in the four protein. The term native state is used to describe the protein in its most stable natural conformation in situ. 3 - What are the structural differences between RNA.
As protein structure has been studied in more detail several sub-levels of structure have been added. Describe how protein structure influences its function. B The secondary structure is the 3-D arrangement of the right-handed alpha helix shown here or alternative structures such as a beta-pleated sheet.
C The tertiary structure is the 3-D folding of the alpha helix show as a. The simplest level of protein structure primary structure is simply the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain. The insulin molecule shown here is cow insulin although its structure is similar to that of human insulin.
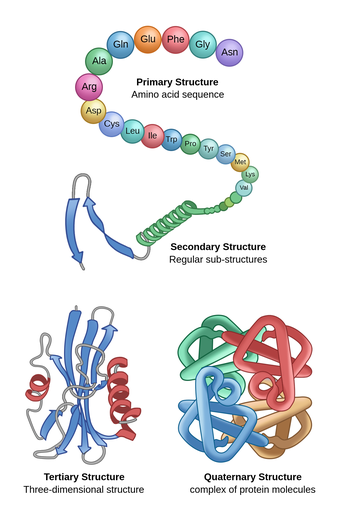
Protein Structure Labster Theory
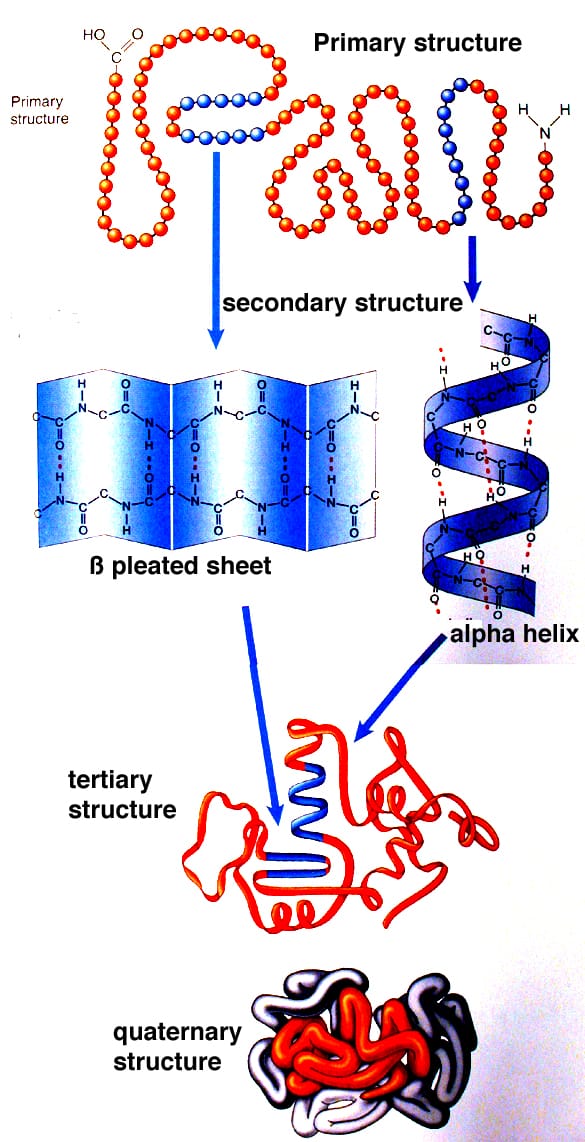
Protein Structures Primary Secondary Tertiary Quaternary Schoolworkhelper

Protein Structure Jpg 682 1 000 Piksel Biochemistry Biology Classroom Teaching Biology

Secondary Supersecondary Structure Of Proteins Biochemistry Chemical Science Chemical Structure

Levels Of Protein Organization

The Four Levels Of Protein Structure Do You Have A Struggling Student Who Needs A Visual Aid To Unders High School Science Biology Resources Secondary Science
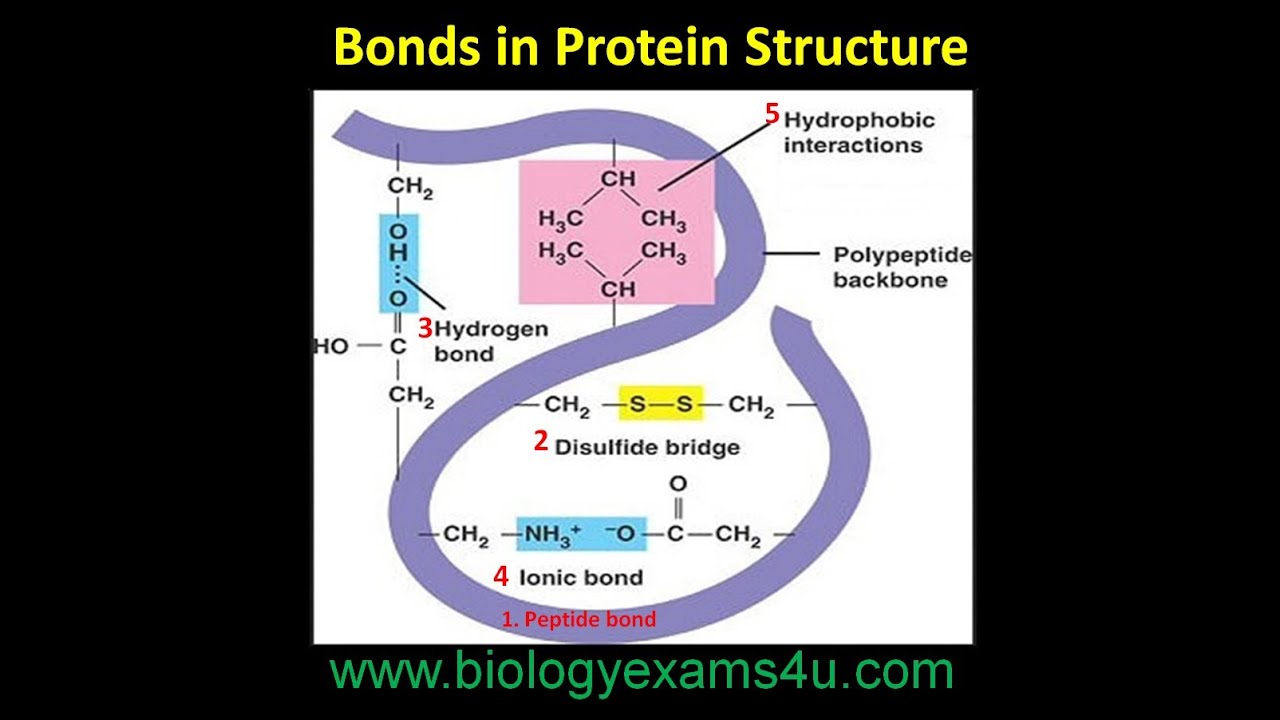
5 Types Of Bonds In Protein Structure Simplified Summary Peptide Bond Biology Lessons Biochemistry

Protein Structure Introduction To Chemistry

Proteins And Protein Structure Biology Doodle Diagram Study Biology Biology Biochemistry Notes

Learn About The 4 Different Types Of Protein Structure Protein Biology Biochemistry Teaching Biology

Openstax Cnx Protein Biology Hydrogen Bond Intermolecular Force
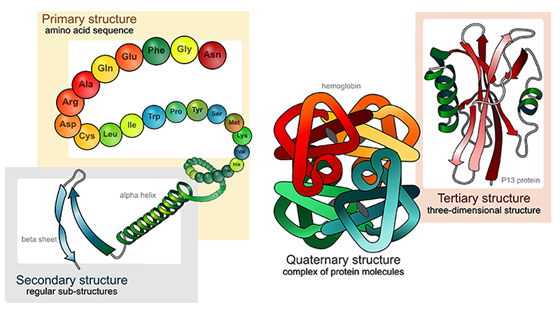
Four Types Of Protein Structure Primary Secondary Tertiary Quaternary Structures

Forces Stabilizing Proteins H Bonds Which Are Key To Protein Structure Are Not That Big Of A Contrib Biochemistry Medical Laboratory Science Science Biology

Major Differences Com Biochemistry Biochemistry Notes Protein Biology
Four Levels Of Protein Structure

Levels Of Protein Organization

Learn About The 4 Different Types Of Protein Structure Protein Biology Protein Fun Science

What Is Protein And Why Do You Need It Biochemistry Biology Notes Protein

Comments
Post a Comment